Maintenance of healthy vascular endothelial cells should help prevent atherosclerosis, a pathological condition caused by damaged vascular endothelial cells affected by elevated levels of blood glucose, cholesterol, oxidative stress, and inflammation. Epidemiological studies have demonstrated that the generation of healthy vascular endothelial cells can be promoted by various methods, including regular physical activity. However, the molecular mechanisms by which exercise exerts this effect are yet to be fully clarified.
Along with researchers at Waseda University, the National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health, and the University of Iowa, Associate Professor Mitsuharu Okutsu and Researcher Mami Yamada (Research Fellow of Gakushin) of the Graduate School of Science at Nagoya City University reported, for the first time, that regular exercise can positively influence the autophagy of vascular endothelial cells via the optimization of interleukin 1 (IL1) action. As disrupted vascular endothelial cell homeostasis is associated with the development of cardiovascular diseases, including atherosclerosis, the findings of the study, published in the FASEB Journal, contribute to preventive medicine and health science.The results will be useful in developing exercise programs and novel drugs that optimize the action of IL1 on vascular endothelial cells and autophagy.
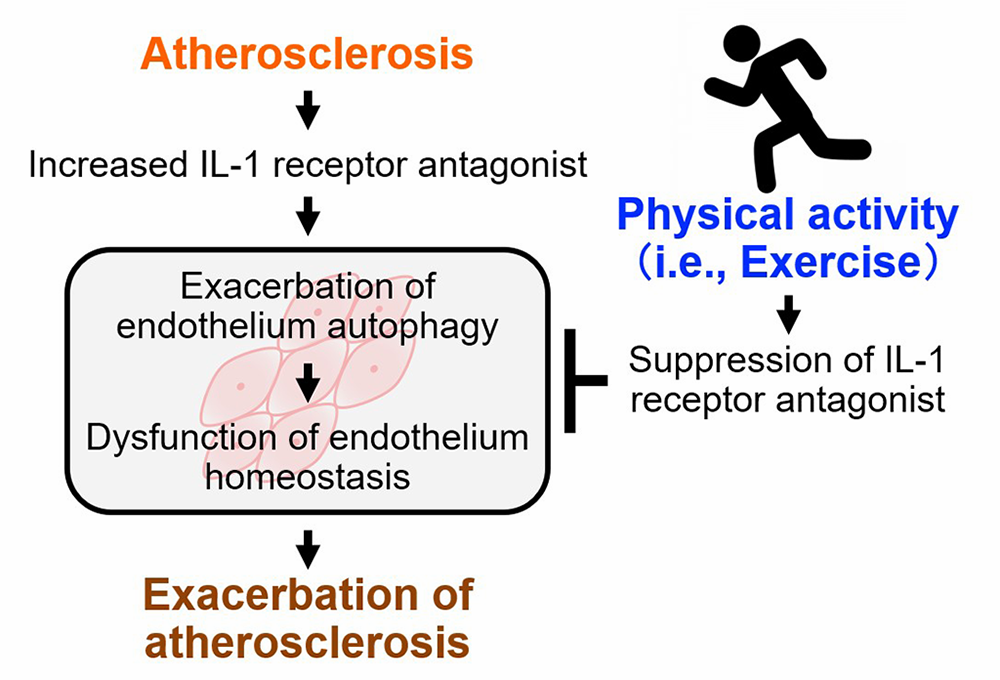
Using an atherosclerosis model (ApoE-deficient mice), the researchers assessed the levels of approximately 50 cytokines that reportedly fluctuate in response to inflammation. As a result of this assessment, it was found that serum levels of IL1 receptor antagonist (IL1ra) were elevated in atherosclerosis but suppressed by regular exercise.
This indicated that elevated IL1ra could inhibit the action of IL1 on cells expressing IL1 receptors. Therefore, using cell cultures with recombinant IL1 protein, the researchers investigated the effects of IL1 on vascular endothelial cells and found that the recombinant IL1 protein promoted autophagy.
Credit: Nagoya City University
The onset of atherosclerosis is associated with the reduced autophagy of vascular endothelial cells. The results of this study suggest that exercise inhibits atherosclerosis via the optimization of the action of IL1 on vascular endothelial cells and the suppression of IL1ra expression. Thus, exercise promotes autophagy and the generation of healthy vascular endothelial cells. These findings are expected to contribute to the development of exercise programs, as well as novel drugs that target this mechanism.
This article has been translated by JST with permission from The Science News Ltd.(https://sci-news.co.jp/). Unauthorized reproduction of the article and photographs is prohibited.




