Due to the outbreak of the new coronavirus disease (COVID-19), there are concerns about an increase in alcohol consumption brought about by social distancing, the lockdown of cities, and stress caused by the economic crisis. The World Health Organization and other authorities have issued warnings regarding these developments. Indeed, an increase in the marketing and consumption of alcohol has also been reported in Japan and abroad. A research group consisting of Professor Yuichi Imanaka, Associate Professor Susumu Kunizawa, and PhD student Takashi Itoshima of the Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto University, has confirmed that the COVID-19 pandemic has increased the hospitalization rate for alcohol-related liver disease and pancreatitis by about 1.2 times. The hospitalization rate for women is increasing rapidly, so women may be more financially affected. These findings were published in Scientific Reports.
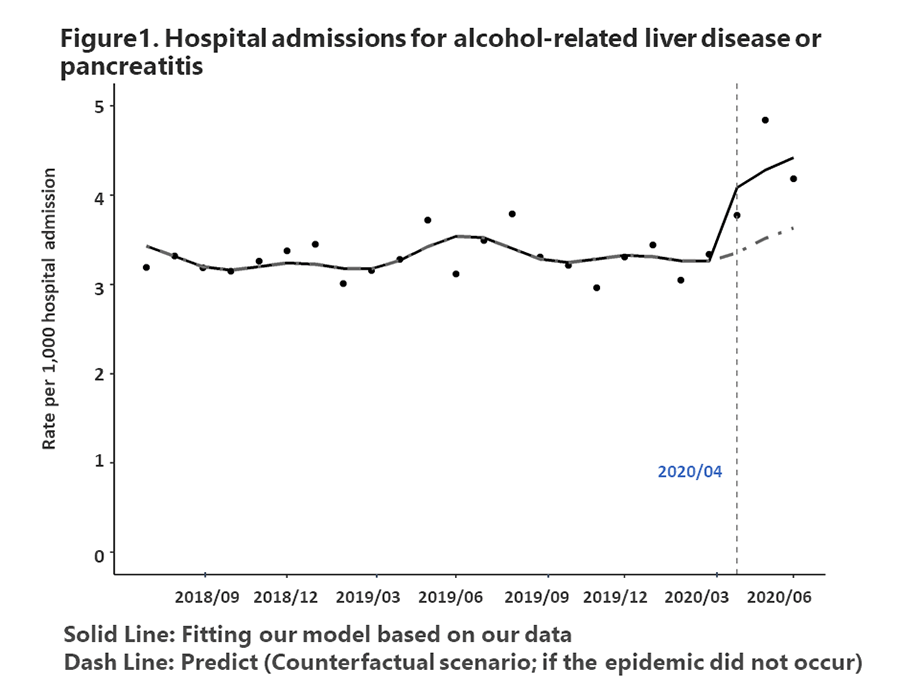
Worldwide, alcohol abuse causes approximately 3 million deaths each year. Stress from the COVID-19 pandemic has raised concerns about increased alcohol consumption globally, and the WHO and other authorities have issued alerts about the risks of alcohol consumption. In fact, reports from the United States and the United Kingdom suggest that alcohol sales and consumption have increased. According to a survey administered by the government of Japan, household alcohol expenditure has been increasing since April 2020. However, the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on hospitalizations for alcohol-related hepatic diseases and pancreatitis is still poorly understood. With these trends as a background, the study group used the QIP (Quality Indicator/Improvement Project) database to examine monthly admission rates per 1000 admissions for alcohol-related liver diseases and pancreatitis from July 1, 2018 to June 30, 2020.
The results of this examination showed that the hospitalization rate during the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic from (April to June 2020) was approximately 1.2 times greater than that during the pre-pandemic period (July 2018 to March 2020). Among the diseases that were reported to cause hospitalization, alcoholic cirrhosis was the most frequent. In addition, the effect of alcohol on the body differs depending on sex. Since it has been reported that the amount of alcohol consumed during the COVID-19 pandemic was also impacted by sex, the analysis targeted this characteristic as well.
The total number of hospitalized male patients is greater than that of female patients, meaning the hospitalization rate itself is also greater. However, when comparing the change in monthly hospitalization rates from 2019 to 2020, the rate increased by 1.1 times in April, 1.2 times in May, and 1.2 times in June for men. In comparison, the rate increased by 1.4 times in April, 1.9 times in May, and 2 times in June for women, a greater rate of increase than that for men. Increased alcohol consumption has also been associated with mental stress from economic crises, suggesting that women may be more economically affected in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. These results may reflect differences in the economic impact of sex, in addition to that of biological differences.
Credit: Kyoto University
Professor Imanaka said, "There are reports that alcohol consumption is increasing due to the COVID-19 pandemic. In this study, using a large-scale database, we have shown that the COVID-19 pandemic may be associated with an increase in hospitalization rates for alcohol-related liver diseases and pancreatitis. Until the COVID-19 pandemic has subsided, alcohol-related liver disease and pancreatitis may continue to increase, and caution should be exercised when consuming alcohol during this period of self-restraint."
This article has been translated by JST with permission from The Science News Ltd.(https://sci-news.co.jp/). Unauthorized reproduction of the article and photographs is prohibited.




