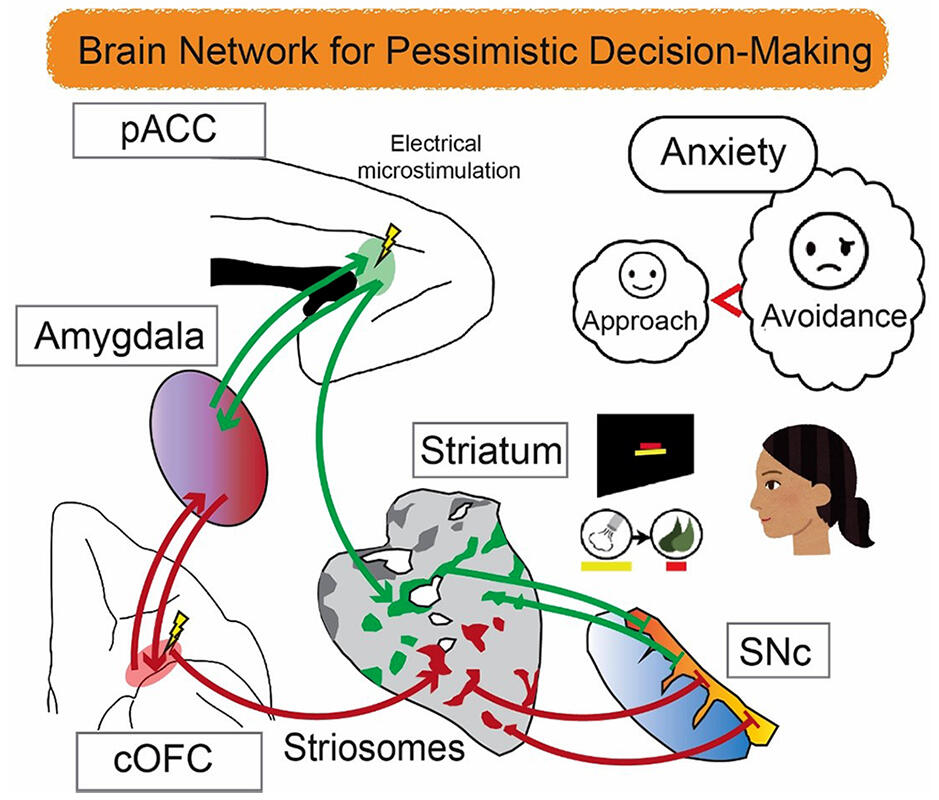
In anxiety disorders, the limbic cortex and basal ganglia are known to act in concert to form large-scale brain networks. A research group that includes Associate Professor Ken-ichi Amemori and Researcher Satoko Amemori, of the Institute for the Advanced Study of Human Biology (WPI-ASHBi), Kyoto University, has previously shown in experiments with monkeys that striatal striosome structures and local pathways in the frontal cortex are involved in inducing pessimistic decision-making, which is influenced by anxiety. In light of this finding and related literature, they have presented a hypothesis about the brain network of pessimistic decision making.
Previous studies by the research group have shown that activation of the anterior cingulate cortex (pACC) and the caudal orbitofrontal cortex (cOFC) by microstimulation induces anxiety-like conditions that affect decision-making. When viral tracers were injected into these regions, the researchers found that the pACC and cOFC project to shared structures, including striosomal structures in the striatum, the caudal part of the caudate nucleus, the medial prefrontal cortex, the amygdala, and the thalamus. In rodents, striosomes project directly onto substantia nigra dopamine-containing cells. Based on this finding, it was hypothesized that the brain regions related to pessimistic judgment may consist of striosomes that control dopamine function and large brain networks that include cortical regions projecting onto them.
Credit: ASHBi - Kyoto University
Three techniques were used to prove these hypotheses: (1) microstimulation using a low level electrical pulse to identify brain regions that are causally involved in pessimistic decision-making; (2) place a virus tracer in those regions to clarify anatomical connectivity; (3) visualize all parts of the brain involved in pessimistic decision-making by performing micro-electrical stimulation with MRI. This revealed the neural connectivity and functional connectivity relationships between brain sites causally involved in pessimistic decision making. The results of this research, which clarified the brain networks related to anxiety, suggest the possibility of specialized treatment for diseases involving specific brain circuits, such as anxiety disorders.
Amemori commented on the outcome, saying, "Through this research we have identifed genes that are specifically expressed in nerve cells involved in anxiety pathways, and we have associated striosomes and their extended network with decision making when faced with anxiety. Ultimately, we hope that this study will be useful toward developing brain pathway-specific treatments for neurological and psychiatric disorders in humans."
■ Striatal striosome structures: The patch structure present in the striatum is divided into a striosome structure and a matrix structure, which have different neurochemical properties.
■ Viral tracer: An anterograde adeno-associated virus with a promoter that infects all cells and a fluorescent protein that serves as a label. It is used as a nerve tracer.
This article has been translated by JST with permission from The Science News Ltd.(https://sci-news.co.jp/). Unauthorized reproduction of the article and photographs is prohibited.




