The research group comprised of graduate student Kazunosuke Ikeno, Associate Professor Tomohiro Fukuda, Professor Nobuyoshi Yabuki , and others from the Division of Sustainable Energy and Environmental Engineering at Osaka University have developed a method for automatically generating building mask images using generative adversarial networks (GAN). These images can be used for training deep learning models using a three-dimensional (3D) model in which aerial photographs of thin clouds generated by the GAN were affixed as texture.
In city planning and construction, researchers use information from aerial photographs to investigate things such as general land use and to confirm the extent of damage in the event of a disaster. Additionally, recent advancements in unmanned aerial vehicle technology have made it possible to acquire a large number of high-resolution aerial photographs in real-time. Image segmentation technology using deep learning is used to validate such large numbers of photographs within a short time. However, in order to perform this, a significant amount of training data is required.
Training data comprises a set of mask images that indicate the target image and the location of the target object in a given image. It is necessary to obtain a large amount of training data of the target with the same characteristics as the target object. However, training data is not available for areas such as local cities and has to be created manually. This means that a bottleneck arises owing to the time and cost associated with the creation of a new dataset. The prototype system developed by the research group creates 3D models from aerial photographs affixed as textures on a general-purpose game engine. Moreover, these models are classified, and by switching the displayed class, the mask images and the aerial photographs, which are the training data, are output from the virtual camera. It then automatically outputs a high-quality dataset by the removing clouds from the aerial photographs using GAN. The dataset generated by the prototype system was trained by a deep learning model, and the building detection accuracy was verified for Sakaiminato City in Tottori Prefecture.
By using this method, it is possible to detect buildings with a higher accuracy via deep learning, even in areas where training data is not currently available. It will also be possible to perform land use surveys and confirm the damage status in the event of a disaster more efficiently. With further advancement of the so-called digital twin (a technology that faithfully reproduces the real world in the virtual world in real time using information acquired from various sensors), the proposed method will be able to be used not only for buildings on aerial photographs, but also for various objects. It is expected that this method will facilitate the automatic generation of training datasets for various objects, such as roads and rivers using aerial photographs. It will also make it possible to view buildings from human perspective images in the future. In addition, the created mask can be used as training data for deep learning and also for visualization, for example, to analyze a city. Therefore, the proposed method is expected to make a great contribution to the field of urban planning and construction.
According to Associate Professor Tomohiro Fukuda, "This research is an interdisciplinary field that spans environmental design (environmental engineering) and computer science (informatics), and we have worked with Kazunosuke Ikeno and Professor Nobuyoshi Yabuki to solve the real-world problems of environmental design (taking humans, buildings, and nature as a series and designing various events surrounding them). We have explored multiple specialized fields for understanding and implementing cutting-edge technologies related to 3D virtual models and deep learning to address the needs and issues in city planning and have attempted to put them together as research results. We hope that the research results will lead to digital transformation towards Society 5.0, its social implementation, and industrialization in the fields of urban planning and environmental assessment."
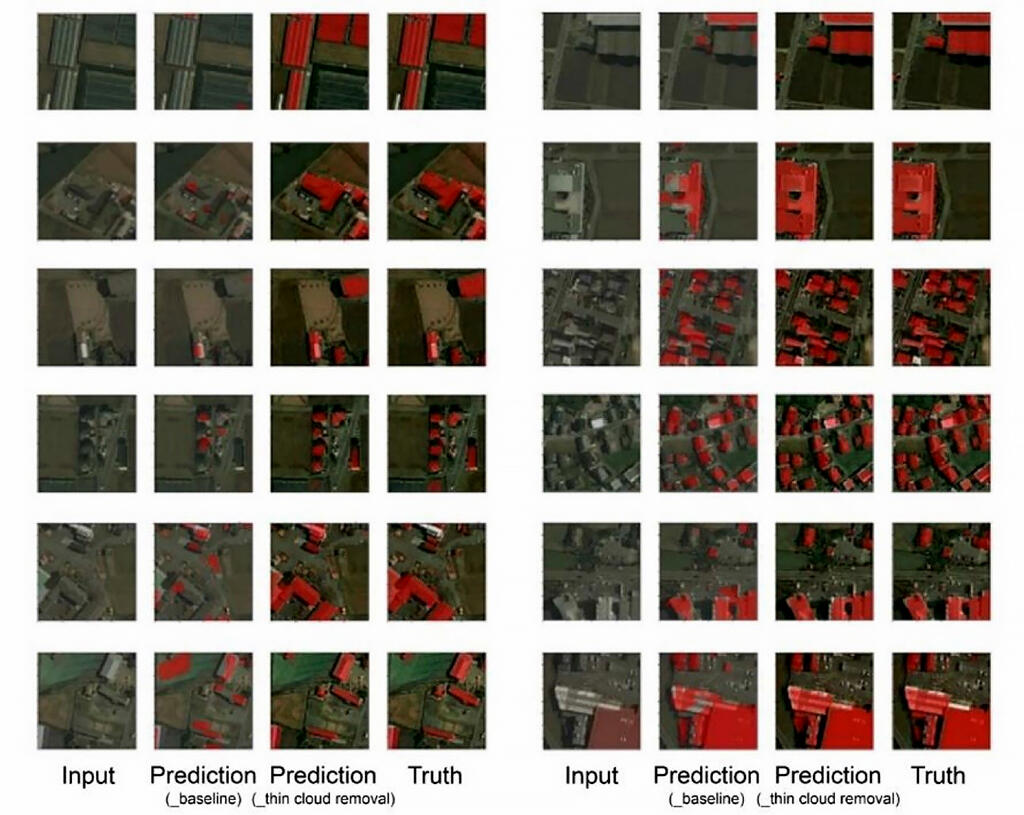
Input: Input image (image including the building to be detected), Prediction (_baseline): Building detection result (when cloud removal by GAN is not performed), Prediction (_thin cloud removal): Building detection result (when cloud removal by GAN is performed), Truth: Correct image
Credit: © 2021 Kazunosuke IKENO et al., Advanced Engineering Informatics
This article has been translated by JST with permission from The Science News Ltd.(https://sci-news.co.jp/). Unauthorized reproduction of the article and photographs is prohibited.




