The National Institute of Information and Communications (NICT) has developed a frequency counting system based on a semiconductor-superlattice harmonic mixer for terahertz waves. The terahertz frequency counter, that is a compact and operational at room temperature, is capable of performing ultra-high-precision measurements with an accuracy of 16 digits in a wideband from 0.1 THz to 2.8 THz, which covers the upper frequency band of radio waves. NICT explains that this terahertz counter becomes a vital frequency measurement system for efficiently utilizing the terahertz band, which is often referred to as the undeveloped frequency domain, as a new radio resource for the next-generation information and communication infrastructure, or Beyond 5G / 6G. In the future, NICT intends to employ this technology for the frequency calibration services in response to various needs in the radio wave industry, terahertz research community in the Beyond 5G / 6G era.
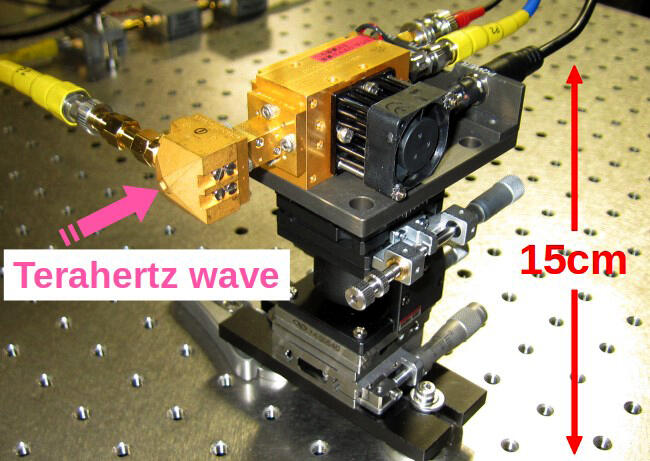
Credit: National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT)
It is expected that the terahertz band will be utilized as a valuable frequency resource for the next-generation information and communication infrastructure, Beyond 5G/6G. In order to use the terahertz band on various industries and researches, a frequency measurement system must be established to fulfill accurate allocation of the terahertz spectrum for both of its proper operation and management, similar to the microwave and millimeter-wave bands as radio resources used for smartphones and similar devices.
However, many terahertz measurement systems reported previously have employed complex ultrashort pulse lasers and bulky cryogenic refrigerators for increasing sensitivity of terahertz-wave detection. This has meant that it is difficult to miniaturize the systems, and the operators have been required to handle the optical equipment including the lasers. In addition to such considerations, the comprehensive evaluation of the measurable frequency band and accuracy of the systems has not been carried out (previous systems reported that the precise measurements were possible, but the operating band was narrow, or the operating band was wide, but the measurement limit was unconfirmed). Therefore, there still existed issues to be tackled for putting the system into practical use.
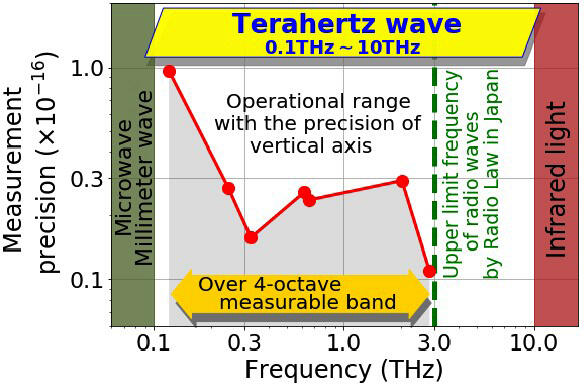
NICT has developed a terahertz frequency counter based on a semiconductor-superlattice harmonic mixer as the novel metrological standard technology for measuring terahertz frequencies, realizing 16-digit measurement accuracy over a 4 octave band from 0.1 THz to 2.8 THz. Such high performance was achieved by adopting a semiconductor harmonic mixer with a superlattice structure, which generate a terahertz comb consisting of multiple harmonics of the input local oscillator in microwave band; The terahertz comb serves as a "precise ruler" in frequency, and thus allows to determine the correct frequency of various terahertz-wave oscillators. This terahertz counter enabled not only eliminating the need for ultrashort pulse lasers, which have been a barrier to downsizing system and reducing operating costs, but also directly referencing microwave signal from the ultra-accurate atomic-clock frequency standard, consequently enabled more stable and reliable terahertz frequency calibration.
Credit: National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT)
As well as significantly reducing its occupied space to approximately 1/40 in comparison with previous systems, this counter has facilitated its actual operation by requiring no expertise in laser technology. Its measurement performance was investigated in detail using test benches designed to mitigate the effect of unavoidable phase noise from terahertz-wave oscillators under test. Such well-designed investigation eventually revealed that the developed counter has a wide measurable range covering the upper frequency band of radio waves defined by the Radio Law of Japan, and a high measurement accuracy of 16 digits; It corresponds to the frequency determination capability of 100 μHz at a 1 THz radio wave, for instance. The above performance is the best reported performance in terms of the operating bandwidth and measurement accuracy of a terahertz frequency counter that is compact, and operates at room temperature.
This article has been translated by JST with permission from The Science News Ltd.(https://sci-news.co.jp/). Unauthorized reproduction of the article and photographs is prohibited.




