A research group led by graduate student Akira Yoshida and Professor Naoko Nakagawa of the Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Ibaraki University, has successfully identified a new formula for numerically quantifying the thermodynamic properties of micro-sized solutions using theoretical methods of modern thermodynamics.
Provided by Ibaraki University
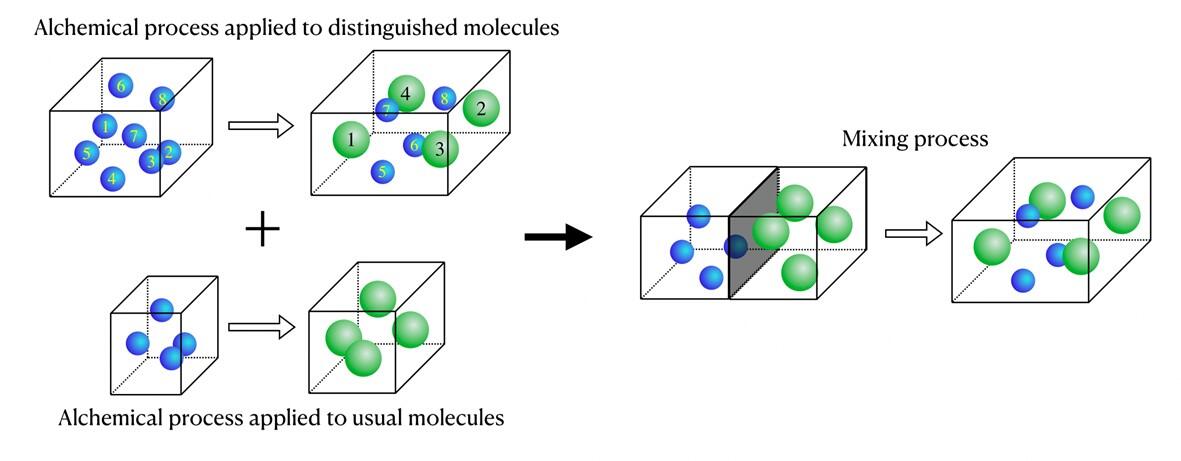
It is a well-known fact that when two or more substances are mixed together, properties that are not present in the original substances appear. By understanding the "mixing free energy" generated in this process, it is possible to predict the new properties brought about by mixing. The mixed free energy formula discovered by the research group was derived by comparing the free energy changes for two different solution preparation methods. One of the two solution preparation processes is the gradual mixing of two pure substances using a semipermeable membrane, which is essentially the same as the everyday act of mixing things. The other is a process to create a mixture that is impossible in reality and can only be achieved through numerical experiments, also known as an alchemical operation. In this process molecular dynamics calculations are first performed using only pure substances that are solvents, and then some solvent molecules are changed to solute molecules during the calculation to create the desired mixture.
The comparison of the two solution preparation processes ultimately revealed that the two alchemical processes, as schematically depicted in the figure above, can be combined to represent mixed free energies. Although the system fluctuates greatly, the Jarzynski equality can be used to determine the free energy change between states. Due to this, the group was able to use this equality to express the free energy change of the two alchemical processes in the figure above, and to use it as a formula to determine the mixing free energy in a micro-sized solution. Using this formula, they calculated the mixing free energy for a mixture of argon and krypton with a total of 500 molecules, and the formula successfully derived the collective effect of a micro-sized system of only 500 molecules as a thermodynamic property.
"The formula we discovered gives us a way to examine numerically whether micro solutions have properties that macro solutions do not," says Professor Nakagawa. "Micro-sized, highly concentrated solutions are a far cry from applying ordinary thermodynamics and reaction kinetics, and the ease with which metastable state domains appear may account for their high reactivity and extensive response to external stimuli. We believe that it is a good idea to use the formulas to determine equilibrium constants for systems in which dissociation and coupling show complex aspects or in which the coexistence of dense and dilute phases produces dynamic fluctuations. I expect it will pave the way for extending reaction kinetics and phase coexistence theory to micro-concentrated systems."
■ Jarzynski equality: An equality that allows the free energy change to be calculated from the amount of work required to change the state of a system with large fluctuations.
Journal Information
Publication: Physical Review Research
Title: Work relation for determining the mixing free energy of small-scale mixtures
DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevResearch.4.023119
This article has been translated by JST with permission from The Science News Ltd.(https://sci-news.co.jp/). Unauthorized reproduction of the article and photographs is prohibited.




