A research group led by Associate Professor Wataru Yoshida and Professor Toru Matsui of the School of Bioscience and Biotechnology at Tokyo University of Technology has succeeded in developing a simple and rapid method for measuring the hydroxymethylation level of genomic DNA, a promising biomarker for cancer and central nervous system diseases, by simply by mixing reagents.
Provided by Tokyo University of Technology
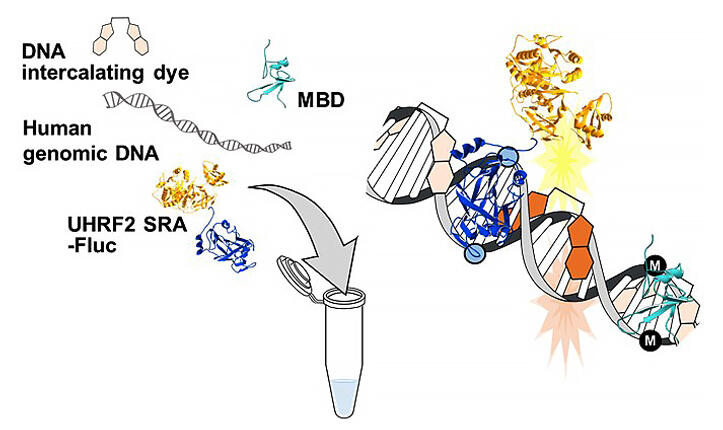
5-hydroxymethylcytosine is an intermediate product of DNA demethylation reaction that has been reported to be a biomarker for central nervous system diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, but there has been no easy way to measure it. The research group has previously developed a method for measuring methylated CpG levels in genomic DNA using methyl CpG-binding protein fusion luciferase. The method developed in this study uses the bioluminescence resonance energy transfer between a DNA intercalator bound to genomic DNA and methyl CpG-binding protein fusion luciferase.
To measure the level of hydroxymethylation, the group focused on the SRA domain of UHRF2, a hydroxymethylated CpG-binding protein. First, a protein (UHRF2 SRA-Fluc) was recombinantly produced by fusing UHRF2 SRA with firefly-derived luminescent protein luciferase. Since UHRF2 SRA binds not only to hydroxymethylated CpG but also to methylated CpG, MBD, a methylated CpG binding protein, was also produced recombinantly to inhibit the binding of UHRF2 SRA to methylated CpG.
Next, they prepared human genomic DNA coupled with a DNA intercalator and MBD, and then added UHRF2 SRA-Fluc and a luciferase luminescent substrate. Their results showed that UHRF2 SRA-Fluc emits light at hydroxymethylated CpG sites in human genomic DNA and excites nearby intercalators. They also found the intensity of the fluorescence to be dependent on the level of hydroxymethylation of human genomic DNA.
This confirmed that hydroxymethylation levels could be measured within 40 minutes simply by mixing target genomic DNA with UHRF2 SR-Fluc, MBD, an intercalator and luciferase luminescent substrate, and then measuring fluorescence intensity.
"The advantage of this method is that if you construct a luciferase fusion protein with a protein that recognizes a specific modified base, you can measure that modified base on the same platform," says Dr. Yoshida. "Furthermore, by fusing luciferases with different maximum emission wavelengths, it is possible to simultaneously measure multiple modified bases. Moving forward, we want to develop a method to measure various modified bases and establish diagnostic methods for diseases related to abnormalities in the state of these modified bases."
■ Hydroxymethylation: A reaction in which methylcytosine is oxidized by methylcytosine oxidase to form hydroxymethylcytosine.
■ CpG: DNA consisting of contiguous sequences of cytosine and guanine.
Journal Information
Publication: Analytical Chemistry
Title: Quantification of Global DNA Hydroxymethylation Level Using UHRF2 SRA-Luciferase Based on Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer
DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.1c05619
This article has been translated by JST with permission from The Science News Ltd.(https://sci-news.co.jp/). Unauthorized reproduction of the article and photographs is prohibited.




