A group led by Assistant Professor Kosei Yamauchi of the Faculty of Applied Biological Sciences, Gifu University, has identified a part of the mechanism in quercetin and its derivatives, which are representative flavonoids, that inhibits cancer metastasis by investigating their binding mode to target proteins.
Provided by Gifu University
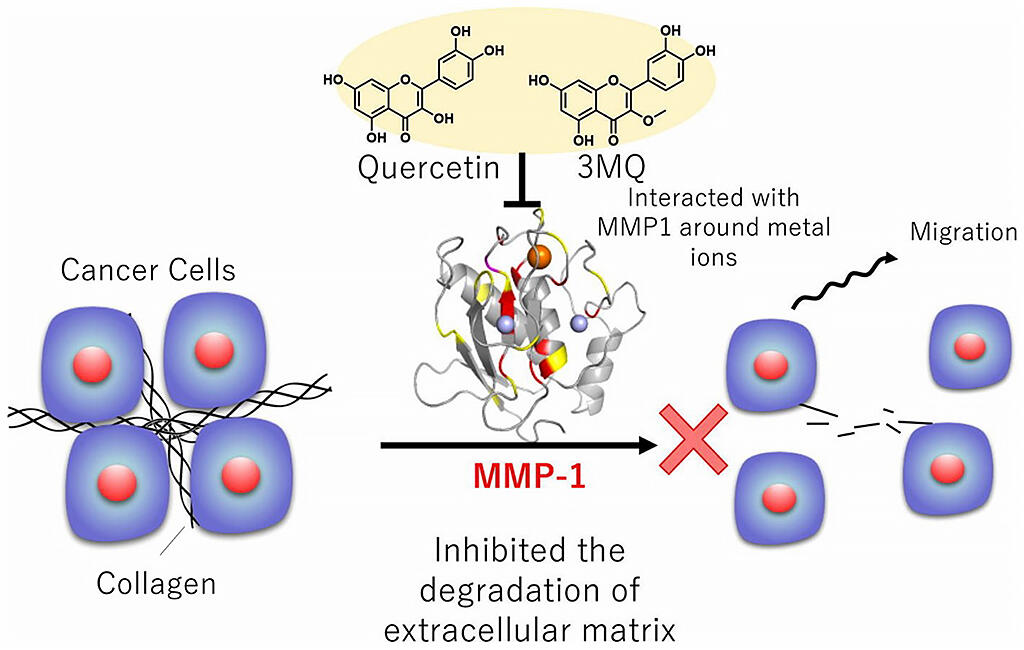
Quercetin is abundant in plants such as onions and citrus fruits, which have been reported to have various biological effects such as anti-inflammatory, anti-obesity and anti-cancer properties, but its mechanism of action is not fully understood. The research group has developed a new synthetic method for flavonoid probes used in pull-down assays in which carrier beads are attached to specific hydroxyl groups of flavonoids (a type of polyphenol widely distributed in plants) to determine target proteins. The probe was used to identify the target protein of the quercetin derivative, and its mode of action was determined by NMR measurements of the protein. Five flavonoid probes were prepared by specifically introducing aminoethoxy groups into flavonoid derivatives.
The group identified MMP-1 as a target protein for quercetin derivatives by a pull-down assay using this synthesized flavonoid probe. They then examined the binding mode of quercetin derivatives to MMP-1 by surface plasmon resonance (SPR) and HSQC (high-resolution two-dimensional NMR measurement method) analysis. SPR analysis confirmed that the interaction between quercetin derivatives and the recombinant MMP-1 catalytic domain was concentration-dependent. They calculated the KD value, which indicates the strength of binding, and found that the derivative (3MQ) bound to MMP-1 more strongly than quercetin. Furthermore, they found that quercetin derivatives inhibit MMP-1 by binding near metal ions, the active center of MMP-1.
These results suggest that quercetin derivatives may inhibit MMP-1 activity and suppress cancer cell migration by binding near metal ions.
"Since it has been suggested that MMP-1 is one of the target proteins of quercetin derivatives in inhibiting cancer metastasis, we believe that we may be able to explore new compounds that inhibit MMP-1," explains Assistant Professor Yamauchi.
■ Pull-down assay: One of the most common methods for investigating proteins that bind to compounds. Proteins bound to the probe produce a precipitate, which is collected for protein analysis. The identification of target proteins of small molecule compounds is crucial in drug design.
Journal Information
Publication: Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry
Title: Development of flavonoid probes and the binding mode of the target protein and quercetin derivatives
DOI: 10.1016/j.bmc.2022.116854
This article has been translated by JST with permission from The Science News Ltd.(https://sci-news.co.jp/). Unauthorized reproduction of the article and photographs is prohibited.




