A research team led by Professor Yutaka Amao of the Research Centre for Artificial Photosynthesis, Osaka Metropolitan University, and graduate student Mika Takeuchi of the Graduate School of Science, Osaka Metropolitan University, combined carbon dioxide with pyruvate, a compound derived from biomass, and used two biocatalysts, decarbonated malate dehydrogenase and fumarate hydratase, to synthesize fumarate, a raw material for unsaturated polyester resin.
Provided by OMU
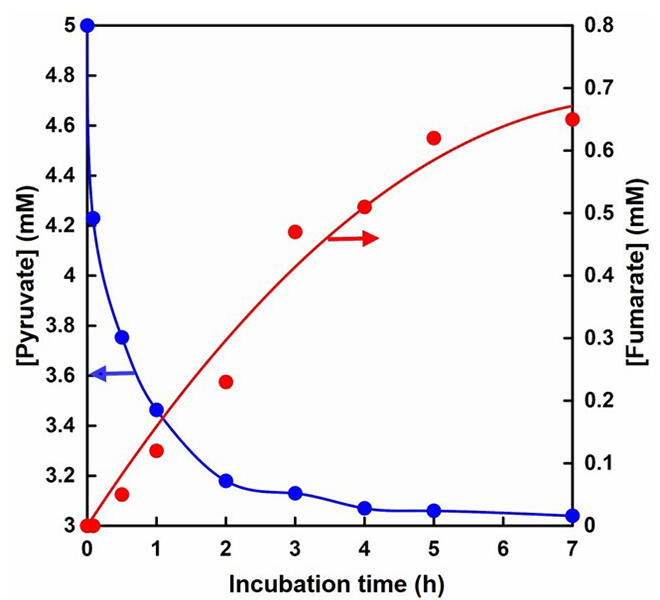
The research team believed that if they could mimic the process of natural photosynthesis, which uses solar energy and carbon dioxide to form glucose, by using carbon dioxide and combining it with organic compounds as raw materials to form durable materials such as plastic products, they could contribute to long-term fixation and reduction of carbon dioxide. As such, they combined carbon dioxide with pyruvate, a biomass-derived compound, using decarboxylated malate dehydrogenase (ME) to produce L-malic acid. They synthesized fumarate by linking the dehydration reaction to L-malic acid using fumarate hydratase (FUM), and about 14% of pyruvic acid was converted to fumarate in a 25-hour reaction. Fumarate is currently synthesized from petroleum as a raw material for polybutylene succinate, a biodegradable plastic, but the results of this research have achieved synthesis with carbon dioxide and biomass-derived compounds.
"We would like to further mimic the process of natural photosynthesis, establish a fumarate synthesis system using carbon dioxide as a raw material using light energy, and further develop the synthesis of biodegradable polymers from the fumarate produced," explains Professor Amao. "In addition, natural photosynthesis uses carbon dioxide as a raw material to synthesize a macromolecule called starch, and our dream is to use artificial photosynthesis to create useful biodegradable macromolecules from carbon dioxide."
This article has been translated by JST with permission from The Science News Ltd.(https://sci-news.co.jp/). Unauthorized reproduction of the article and photographs is prohibited.




