A joint research group led by Associate Professor Haruki Ochi of the Faculty of Medicine, Yamagata University, and Professor Hajime Ogino of the Amphibian Research Center (ARC, Hiroshima University, with the support of Project Associate Professor Akinori Kanai and Professor Yutaka Suzuki (the University of Tokyo) of the Division of Systems Genomics, has clarified the mechanism of renal tubule regeneration in an amphibian model and developed a drug that promotes this regeneration.
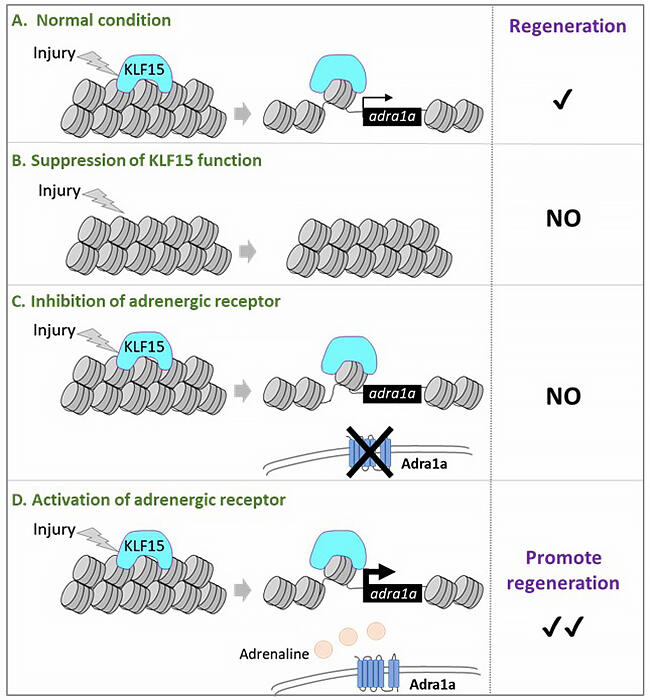
B. Suppression of KLF15 function causes failure of kidney regeneration.
C. Inhibition of Adrenergic receptors causes failure of kidney regeneration.
D. Activation of the Adrenergic receptor promotes the kidney regeneration.
Provided by Associate Professor Haruki Ochi, Yamagata University
The group performed comprehensive open chromatin analysis, epigenetically modified immunoprecipitation sequencing analysis, and total RNA expression analysis on cells from amphibian embryos before injury, during regeneration, and after regeneration of renal tubules. An integrated analysis of this data revealed that the region where chromatin opens during regeneration is a candidate for an enhancer, that KLF is a candidate activator, and that adrenergic receptors are candidate target genes.
The transcription factor KLF is known as one of the four Yamanaka factors (four types of genes proposed by Professor Shinya Yamanaka 's group at Kyoto University for constructing iPS cells). This transcription factor family includes activator, repressor, and bifunctional types with activating and repressing functions. Total RNA expression analysis revealed that among the KLF family members, klf4, klf6, klf15, sp1, and sp4 are expressed in renal tubule cells during regeneration.
When the team investigated whether KLF has transcriptional activating capacity for regeneration-specific open chromatin regions (candidate enhancers), it found that Klf6 and Klf15 work as activators. They next performed amphibian transgenic reporter analysis to investigate whether the regeneration-specific open chromatin region acts as a regenerative enhancer after renal injury. As a result, they found that the regeneration-specific open chromatin region is an enhancer activated in response to renal tubule injury.
They also found that repressing Klf15 function inhibited renal tubule regeneration. Klf15 induces the expression of many genes, one being adrenergic receptors. The team found that the action of adrenergic receptor inhibitors inhibited regeneration in amphibian embryos with damaged renal tubules. Conversely, agonists of adrenergic receptors were found to promote renal tubular regeneration.
Associate Professor Ochi said, "We have only uncovered a portion of the regeneration mechanism. We hope to discover new mechanisms and regeneration-promoting agents through more detailed genome function analysis in the future."
■ Enhancer: In addition to genes, there are non-genetic regions in the genome called noncoding DNA regions. Noncoding DNA regions account for 98% of the human genome and include regions that turn gene expression on and off. Regions that turn on gene expression are called enhancers.
This article has been translated by JST with permission from The Science News Ltd.(https://sci-news.co.jp/). Unauthorized reproduction of the article and photographs is prohibited.




