Cancer is believed to affect one in two Japanese people. Many cancers cause atrophy of fat and muscle throughout the body and extreme weight loss as they progress. Unusually, pancreatic cancer causes weight loss even when it remains localized. However, the mechanism behind this action had not been clarified.
A research group led by Motoyuki Otsuka, a Lecturer of the Department of Gastroenterology, the University of Tokyo Hospital, and Dr. Chikako Shibata, focused on the extracellular vesicles that envelop various physiologically active substances, hypothesizing that extracellular vesicles produced by pancreatic cancer act on fat cells throughout the body, causing lipolysis. They then proceeded to verify this hypothesis. The results confirmed that extracellular vesicles derived from Panc-1 and Miapaca-2 pancreatic cancer cell lines cause fat cell degradation.
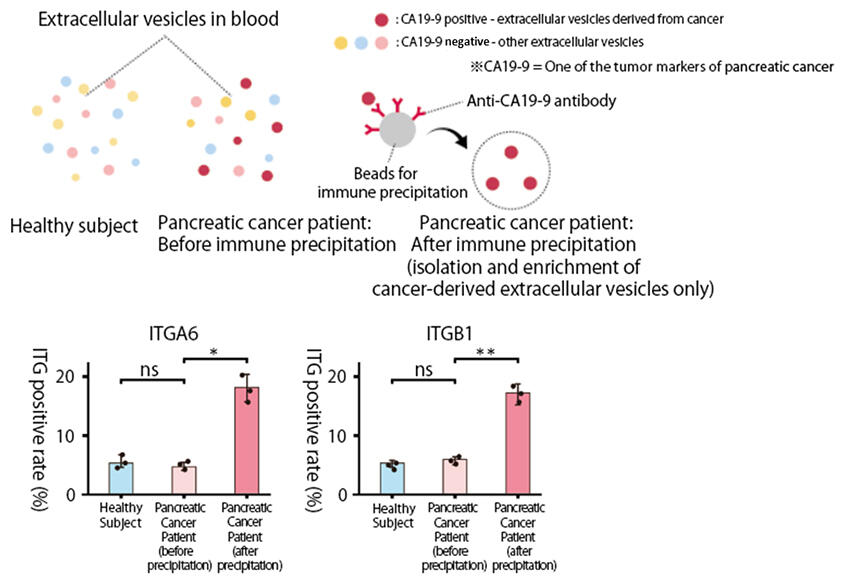
Furthermore, they found that Panc-1-derived extracellular vesicles are readily taken up by fat and the lungs. This action is due to the high expression of ITGB1 and ITGA6 in Panc-1-derived extracellular vesicles, which tend to adhere to fat cells and lungs. The research group has also established a method to isolate and analyze only those extracellular vesicles that are thought to be derived from pancreatic cancer from a heterogeneous group of extracellular vesicles. This method enables detailed analyses that are not possible with conventional batch analysis. Results showed that among extracellular vesicles derived from pancreatic cancer patient blood serum, a significantly higher percentage of vesicles derived from pancreatic cancer expressed ITGA6 and ITGB1 compared to those derived from other tissues. Now that some of the mechanisms behind weight loss in pancreatic cancer have been clarified, the research team next aims to develop and create new therapies targeting cancer-derived extracellular vesicles.