Various hardware candidates are being studied around the world in the race to realize quantum computing. One leading candidate is based on electron spin. This candidate sees a single electron confined in a tiny semiconductor box (or region) as a quantum dot, with its spin used for information processing. The development of fundamental technologies to control spin orientation and readout is progressing rapidly. However, one vital development issue is the integration of quantum dots. Although 2 × 2 and 3 × 3 two-dimensional quantum dot arrays have been reported, quantum dot two-dimensional arrays have not yet been realized for spin resonance using micromagnets, despite this being considered a promising method for controlling electron spin.
To achieve this configuration, a research group led by Associate Professor Haruki Kiyama of the Graduate School of Information Science and Electrical Engineering, Kyushu University, Graduate Student Shungo Nakamura and Professor Akira Oiwa of the Institute of Scientific and Industrial Research, Osaka University, developed a method to design micromagnet shapes for 2 × 2 quantum dots using a numerical simulation of the magnetic field distribution generated by the micromagnets. By optimizing the micromagnet shape, the group estimated an accuracy of over 99% for silicon-based quantum dots, which is expected to provide the high-precision control necessary for error tolerance. The group published a paper in the online edition of the Journal of Applied Physics which was adopted as a Featured Article and cover story.
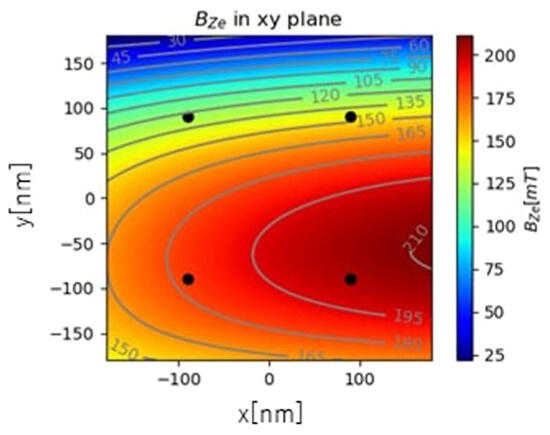
Provided by Kyushu University
Based on the design it has obtained, the research group will work to fabricate a 2 × 2 quantum dot array and micromagnets to enable electron spin control and evaluate its accuracy. It will then expand the method to spin control in even larger arrays, aiming to realize a semiconductor quantum computer in the next 20 to 30 years.
Journal Information
Publication: Journal of applied physics
Title: Micromagnet design for addressable fast spin manipulations in a 2 × 2 quantum dot array
DOI: 10.1063/5.0088840
This article has been translated by JST with permission from The Science News Ltd. (https://sci-news.co.jp/). Unauthorized reproduction of the article and photographs is prohibited.




