A research group led by graduate student Hiroshi Yaguchi (at the time of research), Professor Masatomo Yashima, of the School of Science, Department of Chemistry at Tokyo Institute of Technology, and other researchers has discovered a new oxychloride material that exhibits oxide ion conductivity exceeding that of conventional materials in the low‐temperature range (<200 ℃). The crystal structure at high temperatures as well as high oxide ion conduction and oxide ion diffusion pathways were clarified.
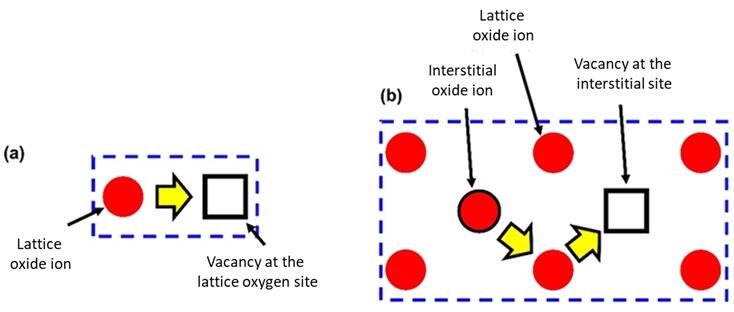
Furthermore, the oxide ion conduction mechanism of the new material was clarified by performing first‐principles molecular dynamics simulations. The results indicated that the new material exhibits high ion conductivity because oxide ions diffuse two‐dimensionally via a quasi‐lattice mechanism, owing to the interstitialcy diffusion of oxide ions through lattice and interstitial oxygen sites. The new oxide ion conductor is chemically highly stable, exhibits constant electrical conductivity over a wide range of oxygen partial pressures, and does not allow electron conduction, which would reduce power generation efficiency.
The bismuth‐containing high oxide ion conductor developed in this research exhibits oxide ion conductivity through the interstitialcy diffusion mechanism, which is different from that followed by conventional bismuth‐containing high ion conductors. Moreover, the study provides new guidelines for the design of oxide ion conductors, thus promoting the development of various new materials. The study is also expected to contribute to the development of high‐performance electrochemical devices such as solid oxide fuel cells that operate at low temperatures by achieving high ion conductivity and stability in the low‐temperature range. These results were published in the electronic edition of Advanced Functional Materials.
© Wiley, (2023), provided by Tokyo Institute of Technology
Journal Information
Publication: Advanced Functional Materials
Title: High Oxide‐Ion Conductivity through the Interstitial Oxygen Site in Sillén Oxychlorides
DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202214082
This article has been translated by JST with permission from The Science News Ltd. (https://sci-news.co.jp/). Unauthorized reproduction of the article and photographs is prohibited.




