NTT and Ajinomoto have announced on May 31 that they entered into a basic agreement to collaborate toward building a platform for promoting the improvement of the well-being and extension of the healthy life expectancy of consumers. Such a platform will utilize various types of data indicating food habits and physical conditions, through converging NTT's "IOWN (Innovative Optical and Wireless Network)-related technologies, such as device development, digital twin computing, and behavior change," Ajinomoto's "AminoScience for food and health."
Provided by Ajinomoto Co., Inc.
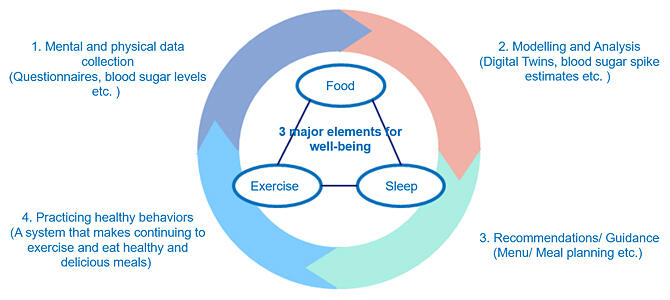
There is a growing concern over the increasing prevalence of lifestyle diseases, attributed to the Westernization of diets and other factors. Regarding lifestyle diseases in Japan, approximately 2.3 million, 1.5 million, and 6 million patients have diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, and hypertensive diseases, respectively. Given this situation, there is a growing sense even among healthy people to improve their dietary habits to prevent lifestyle diseases. The two companies believe that in order to change behavior in a way that is easy to engage in and continue, it is necessary to propose dietary habits that accompany the joy of eating and are tailored to individual consumers.
Through this agreement, the two companies will collaborate in the creation of a business model that utilizes data on the dietary content of consumers and those on their bodies, such as blood sugar levels, predicts their physical conditions and feeling of satisfaction, proposes dietary habits that will have a positive impact on health while increasing food satisfaction, and advances the practice of such habits. The companies also aim for the social implementation of the services developed by the collaboration through government and business partnerships.
This enterprise will integrate the technologies and know-how of both companies to work out a practice that enables people to comfortably follow the cycle of exercise, sleep, and dietary behaviors needed for maintaining good health. For example, the companies conduct research on the correlation between dietary behavior based on personal factors and lifestyle disease risk reduction. When acquiring blood sugar profiles and other data using wearable sensors, data such as dietary content records are obtained and analyzed along with various types of vital data.
This will enable the visualization of the correlation between dietary behavior based on personal factors and reduction of risk of lifestyle diseases, and the demonstration of the improvement effect of recommendations (recommended diets) based on the identified correlation.
Moreover, the companies define 'well-being model of food' as a model by which recommendations according to individual circumstances are provided based on data on consumers' food preferences, values, and dietary content records. Thus, such a model can lead to dietary behavior change and increased satisfaction.
Furthermore, utilizing AI technologies and verification platforms provided by NTT DATA to support the personalization of food and health, the clarification of the correlation between food and well-being, as well as model building, will be carried out for improving the method of enhancing well-being in daily life through food.
The two companies will start a demonstration process to visualize the correlation between dietary behavior and risk reduction of lifestyle diseases based on personal factors. They will then proceed with a demonstration to maximize individual well-being and health effects through recommendations based on the above correlation. Finally, they will incorporate the findings via digital twin computing and other systems to be implemented in society as a service platform.
This article has been translated by JST with permission from The Science News Ltd. (https://sci-news.co.jp/). Unauthorized reproduction of the article and photographs is prohibited.




