Body odor in some people causes allergic symptoms such as coughing and sneezing in people who are in their close vicinity. This phenomenon is called 'people allergic to me' (PATM), but its actual features are still unknown. The research groups of Professor Yoshika Sekine of the Department of Chemistry, the School of Science at Tokai University and Mr. Daisuke Oikawa of AIREX measured and analyzed the skin gases of 20 patients with PATM and detected artificial chemicals, sulfur compounds, and other volatile components on the skin surface. They also found that many of the gases diffusing from the skin surface were unpleasant and that the skin gas composition of these patients exhibited features in common. In addition, they suggested that the ability to metabolize chemical substances and oxidative stress are involved in the skin gas composition. The results were published in Scientific Reports as the world's first original article on PATM odorants.
Provided by Tokai University
Human body odor is composed of several volatile compounds emitted from the skin surface. Skin gas is usually perceived as a matter of comfort or discomfort by people nearby, but adverse effects of body odor on human health has been scarcely studied.
However, an increasing number of people have complained recently through social media that their skin gases caused allergic reactions such as sneezing, runny nose, coughing, itchy eyes, and bloodshot eyes in other people, a phenomenon known as PATM. Many patients with PATM may also experience psychological anxiety, which may force them to quit their jobs. However, the studies focused on PATM are lacking, and the actual situation is unknown.
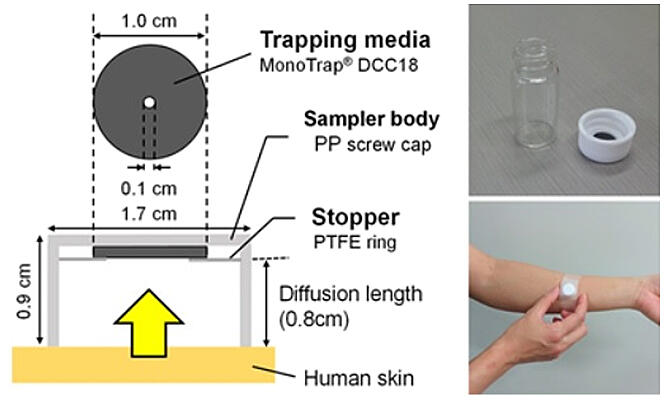
The research group used a passive flux sampler and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry to measure the emission and characterize the composition of 75 skin gases from those who claimed to have PATM. The PATM group showed large emissions of artificial chemicals like toluene, xylene, sulfur-containing compounds such as methyl mercaptan, and hexanal, which has an anxiety effect, whereas the emission of aroma compounds was relatively low.
Although it is presently difficult to demonstrate the mechanism to explain the characteristic skin gas composition in the PATM group, the ratio of toluene to its metabolite benzaldehyde is considered a vital sign of PATM. This ratio may be associated with the activity of cytochrome P450 superfamily, which are drug-metabolizing enzymes in the liver. In addition, hexanal is a possible oxidation product of sebum, and its release may be related to oxidative stress. The emitted amount was at a level that affected the body odor of those claiming PATM.
Sekine said, "The phenomenon or symptom of PATM has so far not been a research subject. However, many people actually suffer from PATM. In this study, the chemical analyses of skin gases that cause body odor revealed that there are common characteristics in the skin gas composition of those complaining of PATM. We hope that the results of our research will lead to the scientific and medical investigations to the cause of PATM."
Journal Information
Publication: Scientific Reports
Title: Human skin gas profile of individuals with the people allergic to me phenomenon
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-36615-1
This article has been translated by JST with permission from The Science News Ltd. (https://sci-news.co.jp/). Unauthorized reproduction of the article and photographs is prohibited.




