A research group led by Professor Yu Matsuda, and Graduate Students Tomoki Inoue and Koyo Kubota of the School of Science and Engineering at Waseda University, Professor Hiroki Nagai and Assistant Professor Tsubasa Ikami of the Institute of Fluid Science at Tohoku University, and Professor Yasuhiro Egami of the Aichi Institute of Technology announced that they have developed a clustering (grouping) method for large amounts of data using quantum-inspired technology. The clustering of large-sized and large amounts of time-series data is viewed as a combinatorial optimization problem, and computation techniques specialized for this problem are applied to achieve high-speed computation.
The group constructed an algorithm that excludes, from any cluster, outliers that are not suitable. It is expected to be applied to and streamline the analysis of time-series data, including images, in a wide range of fields such as weather, life sciences, and economics. The results were published in the international academic journal Communications Engineering on January 10, 2024.
Provided by Waseda University
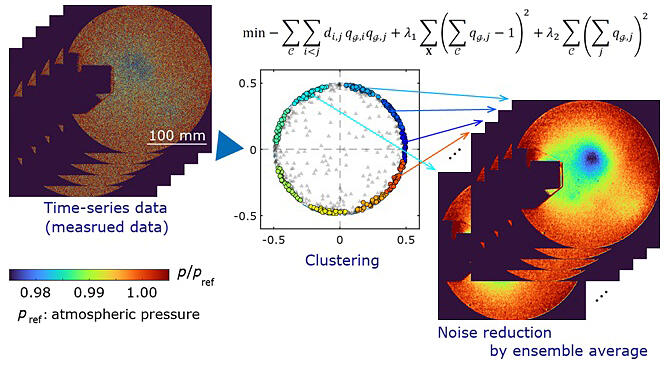
Time-series data are collected in numerous fields including science, engineering, the environment, agriculture, life sciences, and economics. The method of clustering time-series data is called "time-series clustering". Recently, it has become necessary to cluster huge sets of data at high speed. Clustering can be thought of as a "combinatorial optimization problem." This makes it possible to utilize new computational technologies that are attracting a lot of attention, such as quantum computers that specialize in combinatorial optimization problems, making it possible to perform high-speed calculations. They devised a way to avoid including outliers in the cluster.
They developed a clustering method that imposes the following three constraints.
- 1) The sum of similarities between data in a cluster increases.
- 2) One data item can be in at most one cluster.
- 3) The number of data entering each cluster and its variance are adjusted.
The developed method is a combinatorial optimization problem that considers combinations of data to meet the conditions. A new computing technology called "Fujitsu Digital Annealer" (a computing technology inspired by quantum phenomena that Fujitsu offers as a service) was used specifically for this calculation.
Clustering was also performed on a dataset that is publicly available online to check its performance on general data. The results confirmed that the method gives results comparable to existing methods.
Matsuda said, "A large amount of data is now being acquired due to improvements in measurement and data storage technologies. In this research, we proposed a method for post-processing measurement data by utilizing computational technology using quantum-inspired technology."
Journal Information
Publication: Communications Engineering
Title: Clustering method for time-series images using quantum-inspired digital annealer technology
DOI: 10.1038/s44172-023-00158-0
This article has been translated by JST with permission from The Science News Ltd. (https://sci-news.co.jp/). Unauthorized reproduction of the article and photographs is prohibited.




