A research group led by Distinguished Professor Hirofumi Tachibana and Assistant Professor Motofumi Kumazoe both of the Faculty of Agriculture at Kyushu University has clarified the mechanism behind a phenomenon where liver fibrosis is suppressed when the number of intestinal bacteria that metabolize soybeans is high. These findings were published in iScience.
Provided by Kyushu University
With an increase in processed food in diets and an associated increase in obesity rates, liver fibrosis has become a worldwide problem. As liver fibrosis causes cirrhosis and hepatic cancer, the establishment of effective prevention and treatment methods is of high importance.
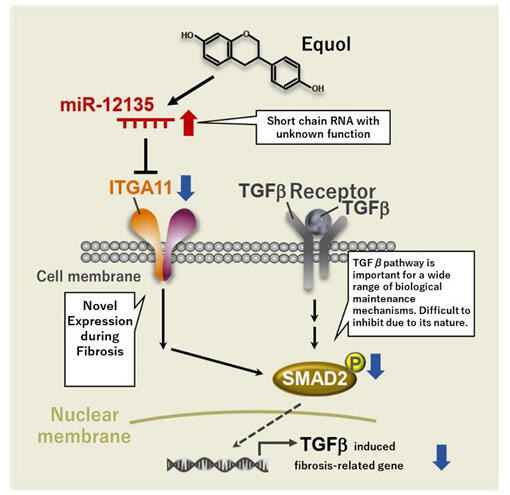
Equol, a type of polyphenol, is produced when soy isoflavones are metabolized by intestinal bacteria. However, the ability to produce equol depends on the intestinal microflora of the individual. It has been reported that liver fibrosis progresses more slowly in patients who can produce equol in their intestines than in those who cannot. However, the specific mechanism behind this phenomenon was unknown.
The research group found that miR-12135, a microRNA of unknown function, exerts a potent inhibitory effect on liver fibrosis. They also found that equol increases the expression of this microRNA. In clarifying the mechanism of action, the researchers further confirmed that miR-12135 exerts its antifibrotic effect by suppressing the expression of a collagen receptor called integrin subunit alpha 11 (ITGA11).
Although the transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ) pathway is known to play an important role in fibrosis, the sustained inhibition of this pathway is not feasible because it is also important for maintaining many normal biological processes. In this study, ITGA11, the expression of which is specifically upregulated during fibrosis, was found to be essential for aberrant activation of the TGFβ pathway. Therefore, targeting ITGA11 is expected to provide safe regulation of the TGFβ pathway.
Journal Information
Publication: iScience
Title: miR-12135 ameliorates liver fibrosis accompanied with the downregulation of integrin subunit alpha 11
DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.108730
This article has been translated by JST with permission from The Science News Ltd. (https://sci-news.co.jp/). Unauthorized reproduction of the article and photographs is prohibited.




