On July 4, NTT and Euglena (Minato City, Tokyo Prefecture) announced that they succeeded in establishing the world's first technology for algal breeding by mutagenesis using neutron beam irradiation. This achievement is expected to become a fundamental technology for solving various issues related to climate change by improving the CO2 absorption rate of algae, and breeding and engineering the microorganism to improve their usefulness for various purposes. The results were published in the British scientific journal Scientific Reports on July 3.
Provided by NTT
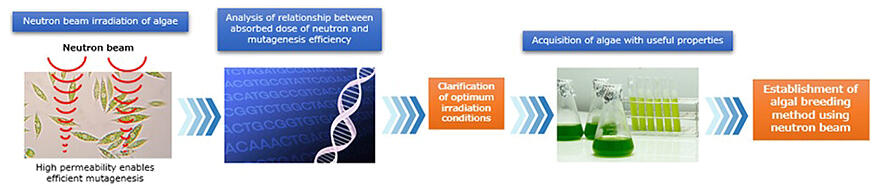
In previously attempted algal breeding methods, gene mutations were introduced using electromagnetic waves and heavy particle beams, which have low permeability to water-containing substances such as culture media. However, these methods were ineffective for most algal cells growing in the culture media. In contrast, NTT and Euglena have focused on neutron beams, which have no electric charge and are highly permeable to water-containing substances. The two companies have been conducting a joint research project on breeding using high-energy neutron beams and thermal neutron beams since 2022.
As a result, they clarified, for the first time, the relationship between the absorbed dose of high-energy or thermal neutron beam and the mutagenesis efficiency of algal genes in this study. The occurrence of mutations was evaluated using the unicellular alga Cyanidioschyzon merolae (Schyzon), based on a mechanism in which a mutation in a gene involved in nucleic acid synthesis allows the cells to grow on agar medium containing a drug that inhibits growth. The analysis revealed that mutations were most effectively introduced when the cells were irradiated with 20 grays (Gy) of high-energy neutrons or 13 Gy of thermal neutrons.
Next, the mutation patterns caused by irradiation under the optimized conditions were analyzed. As a result, of the mutation patterns of the genes in which mutations were introduced, about 90% were accounted for by single-nucleotide substitutions, deletions, and insertions, and about 10% were accounted for by changes of two or more nucleotides. A previous study has reported that changes in two or more nucleotides accounted for about 30% of the gene mutation patterns caused by irradiation with γ-ray, a type of radiation. The present findings suggest that the mutation patterns caused by neutron beam irradiation differ from those caused by the current method. The optimum neutron irradiation conditions identified in Schyzon were applied to a commercial strain of the "microalga E. gracilis," which produces raw lipids for biofuels equivalent to jet and diesel fuels, as an attempt to obtain cells with improved lipid production. A fluorescent dye that specifically stains lipids was added to cells irradiated with neutron beams. The cells were selected using the fluorescence intensity emitted by each cell as an indicator. As a result, four strains producing 1.2−1.3 times higher amounts of lipids than the wild-type strain were successfully obtained. These results confirmed the feasibility of algal breeding by neutron beam irradiation.
NTT has future plans to breed algae with improved CO2 absorption, analyze the genes responsible for this improvement, and verify the effectiveness of expanding this technology to organisms other than the two algae species that have been analyzed.
Journal Information
Publication: Scientific Reports
Title: Optimal conditions of algal breeding using neutral beam and applying it to breed Euglena gracilis strains with improved lipid accumulation
DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-65175-1
This article has been translated by JST with permission from The Science News Ltd. (https://sci-news.co.jp/). Unauthorized reproduction of the article and photographs is prohibited.




