NTT has developed the world's first mirror-transcending aerial imaging system, in which virtual characters in the digital world can move freely in and out of mirrors. The virtual characters are displayed with a high degree of realism inside and outside the mirrors, enabling interactive and intuitive operations. In the future, NTT will continue research and development for enhancing the stereoscopic effect and image quality to improve the realism of aerial images. The corporation will also create new video viewing experiences in spaces where real and virtual images intersect at cultural facilities such as museums and venues for entertainment events.
Provided by NTT
Previously, mirror displays were proposed as a technology for integrating virtual characters into everyday spaces, which generate mirror images by placing a display behind a translucent mirror (half-mirror). This technology enables a virtual character to be displayed alongside the user's own reflection in a mirror. As it draws considerable visual attention, this technology has been adopted in signages and various attractions.
Aerial-image technology, which allows the formation of images in space without the viewer's consciousness of the display, has also been proposed, and has been utilized for live events and sports games. However, these conventional mirror displays, and aerial image technologies limit the displayable area to either inside or outside the mirror. It has been difficult to achieve display that is not bounded by the physical constraints of the mirror surface.
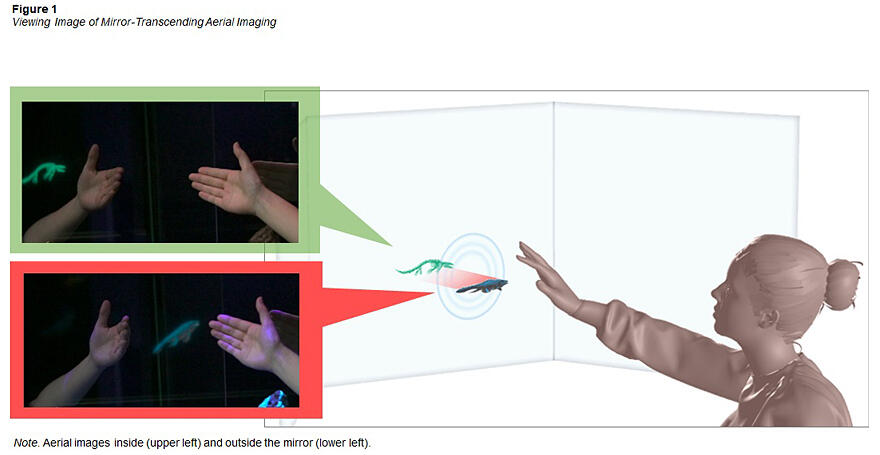
NTT has removed these limitations with a mirror-transcending aerial imaging system that allows virtual characters to move freely in and out of the mirror. Besides providing the conventional mirror display of a virtual character in a mirror, this system invokes a fictional experience in which the virtual character pops out of the mirror, sharing the same space as the users. In the developed system, images from a display equipped with a moving mechanism are formed in space by retroreflection. Therefore, multiple users can simultaneously view an aerial image without wearing VR goggles or 3D glasses.
The first key point of this technology is its optics system, which connect the real and virtual spaces. The light emitted from the display (i.e., the light source) is reflected by the half mirror and then retroreflected by a retroreflective material. A type of reflection by which incident light from a light source is returned as-is directly toward the light source is referred to as retroreflection. A material that possesses such a feature is referred to as a retroreflective material. For example, the retroreflective feature is employed in road signs which direct the light from a vehicle's headlights back to the driver, brightening the letters and surrounding objects.
In the new technology developed by NTT, the retroreflected light passes through a half mirror to form an aerial image in space. As the display is equipped with a moving mechanism, the depth position of the aerial image can be moved back and forth across the central half-mirror. Accordingly, the aerial image appears to continuously move in and out of the mirror, a phenomenon that is unique to mirror-transcending aerial imaging. Furthermore, the half-mirrors can be arranged like a three-sided mirror to expand the viewing range of the aerial images without greatly extending the optical path length until the aerial images are formed. This functionality increases the number of possible viewers.
The second key point of this technology is intuitive interaction. Conventional aerial image technology often enables intuitive interaction with users, such as direct reaching into the aerial image. The mirror-transcending aerial image display system applies this technique to an aerial image displayed outside the mirror. For this system, a method has been conceived for achieving the same intuitive operation on aerial images inside the mirror, which cannot be reached by users.
The conceived system is achieved using a sensor that acquires the position coordinates of the user's hand in real space. When the aerial image is displayed outside the mirror, the aerial image is manipulated using the coordinates of the user's hand as-is. When the aerial image is displayed inside the mirror, the coordinates of the hand reflected in the mirror are calculated to manipulate the aerial image. By switching the coordinates according to the display area of the aerial image, the system allows users to experience intuitive interactions with the aerial image both inside and outside the mirror.
A demonstration of this mirror-transcending aerial display system, showing a virtual character moving in and out of a mirror, can be viewed at the following URL: https://youtu.be/qjwOTF_b1sY
This article has been translated by JST with permission from The Science News Ltd. (https://sci-news.co.jp/). Unauthorized reproduction of the article and photographs is prohibited.




