A research group led by Associate Professor Yuki Matsuura of the Cooperative Faculty of Education, Utsunomiya University, and Professor Yosuke Sakairi of the University of Tsukuba (currently affiliated with Tokoha University) have showed that training combining oculomotor and bimanual coordination exercises immediately stabilized balance in athletes, with a session over approximately 5 minutes being effective. This training is expected to be utilized in warm-up and conditioning exercises before athletes perform. The results were published in the international journal Open Access Journal of Sports Medicine on July 17.
Provided by Utsunomiya University
Balance training in athletes has been shown to help reduce the risk of sports-related injuries and improve functional performance. However, balance training (e.g., standing with one or both legs on stable or unstable surfaces with one's eyes open or closed) performed as a warm-up reportedly does not improve balance stability immediately after training and has a short-term negative effect.
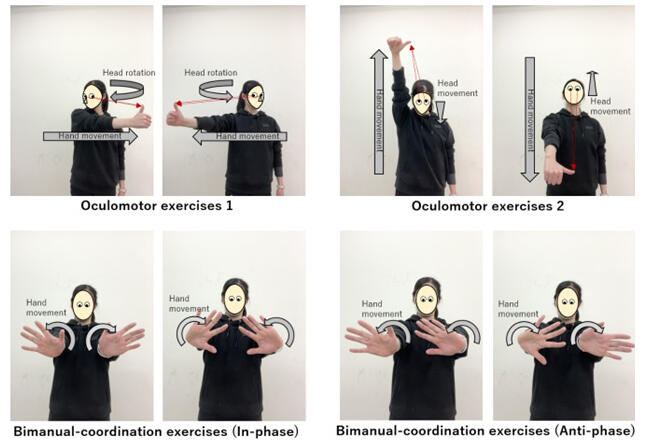
In this study, the research group focused on oculomotor exercises, which reportedly improve balance in the field of rehabilitation for stroke and other disorders, and bimanual coordination exercises, which are related to the activation of the cerebellum that maintains posture and balance. Warm-up exercises to immediately improve balance were examined.
Thirty healthy university student athletes were included in the study. The training program was conducted under the following three conditions (for approximately 5 minutes each) to verify the effectiveness of the program: (1) oculomotor exercises, (2) bimanual coordination exercises, and (3) a combination of oculomotor and bimanual coordination exercises.
The results confirmed that the combination of oculomotor and bimanual coordination exercises in (3) reduced unintentional large sway during balancing and immediately increased postural stability. This exercise, in combination with conventional balance training, is expected to be useful as a training program to provide additional improvement.
Matsuura said, "I, as an active athlete, perform this training, and I have experienced its effectiveness firsthand. In the future, we will examine the effects of this training on actual performance demonstration situations and the effects of conventional balance training combined with the exercises tested in this study."
Journal Information
Publication: Open Access Journal of Sports Medicine
Title: Do Combined Oculomotor and Bimanual Coordination Exercises Instantly Stabilize Balance in Athletes?
DOI: 10.2147/oajsm.s472125
This article has been translated by JST with permission from The Science News Ltd. (https://sci-news.co.jp/). Unauthorized reproduction of the article and photographs is prohibited.




