A research group led by Specially-Appointed Professor (Professor Emeritus) Masahiro Nishibori, Professor Masakiyo Sakaguchi, and Visiting Researcher Yohei Takahashi at the Okayama University Graduate School of Medicine, Dentistry, and Pharmaceutical Sciences has identified C-type lectin family 1A (CLEC1A) as a specific receptor for antithrombin, a plasma protein with anti-inflammatory effects. The results were published in Blood VTH.
Provided by Masahiro Nishibori, Okayama University
Antithrombin has been reported to have anti-inflammatory effects and regulate thrombin activity through direct binding to thrombin. However, the substance involved in its molecular mechanism of action was completely unknown.
In a previous study on the plasma protein HRG, Nishibori's research group has successfully identified a novel HRG-specific receptor. Based on an analogous idea, they hypothesized that there is a plasma membrane receptor associated with anti-inflammatory effects of antithrombin. They used a screening method originally developed by Professor Sakaguchi's research group to search for and identify a novel receptor for antithrombin and analyze its functions. Antithrombin ligand and candidate receptor genes were co-expressed in HEK293T cells, and candidate receptors bound by the ligand were identified through immunoprecipitation. As a result, CLEC1A was identified as a candidate receptor for antithrombin.
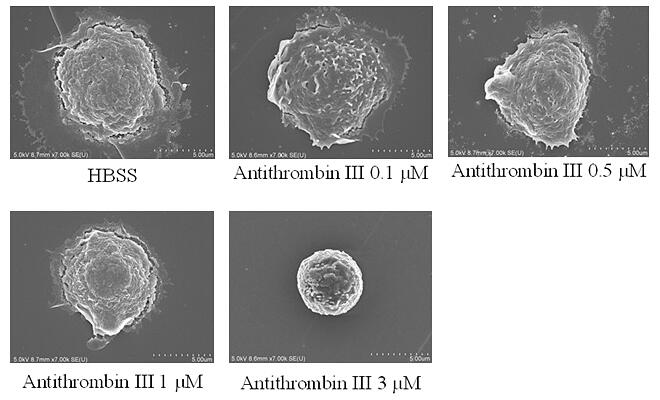
Stimulation of CLEC1A on human neutrophil cells by antithrombin induced morphological changes of neutrophils to a spherical shape with a smooth and regular surface and functionally decreased neutrophil death and reactive oxygen species production. They also demonstrated the involvement of the antithrombin−CLEC1A system in the anti-inflammatory effects of antithrombin. These cellular effects of antithrombin are very similar to those of HRG, for which CLEC1A also serves as a receptor, suggesting a completely new functional role and mechanism of action for the plasma proteins.
Journal Information
Publication: Blood Vessels, Thrombosis & Hemostasis
Title: Antithrombin regulates neutrophil activities through the stimulation of C-type lectin family 1A
DOI: 10.1016/j.bvth.2024.100032
This article has been translated by JST with permission from The Science News Ltd. (https://sci-news.co.jp/). Unauthorized reproduction of the article and photographs is prohibited.




