A research group including Professor Takehisa Hanawa, Assistant Professor Kaoru Hirose, Undergraduate Student Rieko Nitto (at the time of the study), Undergraduate Student Shohtaro Yokota, and Junior Associate Professor Yayoi Kawano (currently professor at Nagoya City University) of the Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences at Tokyo University of Science and MP Gokyo Food & Chemical has announced that they developed a tea catechin-containing gel preparation promising as a new therapeutic agent for oral mucositis (stomatitis). They developed the gel preparation in anticipation of its application as a formulation for treatment of oral mucositis without discomfort. The formulation is safe, as it contains tea catechins and xyloglucan, a common food additive. It also exhibits excellent physicochemical properties. The findings are expected to contribute to the development of therapeutic drugs for stomatitis and were published in the international journal ACS Omega on December 20.
Provided by Tokyo University of Science
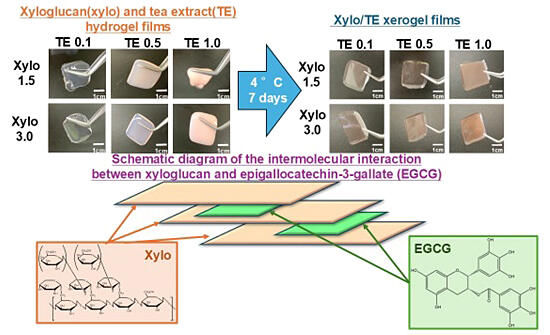
Oral mucositis is an adverse reaction to chemotherapy or radiotherapy. Aphthous stomatitis, in particular, often recurs and causes eating and sleeping disorders because the lesions produce intense pain. Topical medications such as ointments, films, mouthwashes and patches are mainly used for treating oral mucositis; however, these formulations struggle to combine ease of use and effectiveness. Xyloglucan (Xylo) is a water-soluble polymer derived from tamarind seeds. It has passed strict safety review processes in Japan, Taiwan, Korea, China, the United States and other countries and is widely used as a food thickener, stabilizer or gelling agent. Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a catechin derivative extracted from green tea, has also been reported to have antioxidant, antitumor and antibacterial effects and inhibits biofilms. Its application to the treatment of oral mucositis has been investigated.
In this study, the research team aimed to develop a formulation for oral mucositis that is easy and comfortable to use. Gel formulations (Xylo/TE gel films) were prepared from tea leaf extract (TE) and Xylo, and their gelling behavior and various physicochemical properties were evaluated.
The results showed that the gel strength, adhesiveness, water absorption and dissolution rate of EGCG could be modulated by changing the amounts of Xylo and TE. The Xylo/TE gel films also showed high strength and high-water absorption. These data indicate that the Xylo/TE gel films have characteristics similar to those of hydrogel films and adhesion strengths comparable to those of commercial films.
Hanawa said, "Our research aims to create drug carriers with new functions by combining various substances listed in the Japanese Pharmacopoeia, the Japanese Pharmaceutical Excipients, and Japan's Specifications and Standards for Food Additives. This study also makes use of the fact that xyloglucan undergoes gelation when mixed with polyphenols and other substances that have a planar structure. Since the tea catechin preparation used in this study contains multiple catechins, we plan to conduct animal experiments using higher-purity catechins and other studies to evaluate the effectiveness of catechin-containing xyloglucan films for treating oral mucositis, aiming for practical application. I will continue to disseminate the research findings obtained as a result of the active efforts made by our students under the guidance of Assistant Professor Hirose while they are busy with classes and practicums."
Journal Information
Publication: ACS Omega
Title: Preparing and Characterizing of Xyloglucan Films Containing Tea Extract for Oral Mucositis
DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c06410
This article has been translated by JST with permission from The Science News Ltd. (https://sci-news.co.jp/). Unauthorized reproduction of the article and photographs is prohibited.




